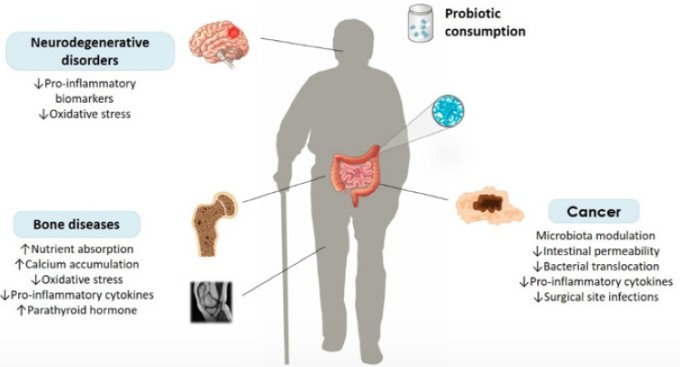
As we age, maintaining a healthy gut becomes increasingly important for digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. Senior citizens often experience changes in gut bacteria due to aging, medications, and dietary shifts. Understanding the roles of prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics can help support a balanced digestive system and enhance overall health.
Understanding Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria. They help nourish and stimulate the growth of these good bacteria, which is especially important for seniors to maintain digestive balance and prevent constipation.
Key benefits of prebiotics for seniors:
- Support digestive health and regular bowel movements
- Improve calcium absorption for stronger bones
- Enhance immune function to reduce the risk of infections
- Promote gut bacteria diversity, which may decline with age
Sources of prebiotics:
- Bananas
- Onions
- Garlic
- Leeks
- Asparagus
- Oats
- Flaxseeds
- Legumes
The Role of Probiotics
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that contribute to a balanced gut microbiome. For seniors, maintaining healthy gut flora is crucial, as aging can lead to a decline in beneficial bacteria, potentially causing digestive discomfort and weakened immunity.
Key benefits of probiotics for seniors:
- Improve digestion and reduce bloating or constipation
- Enhance the immune system, helping to fight off illnesses
- Support mental clarity and cognitive function through the gut-brain connection
- Help manage inflammation, which is linked to age-related conditions
Sources of probiotics:
- Yogurt with live cultures
- Kefir
- Butter Milk
- Kimchi
- Miso
- Cucumber
- Apple
What Are Postbiotics?
Postbiotics are the beneficial byproducts of probiotic activity. When probiotics feed on prebiotics, they produce bioactive compounds that support gut and overall health. For seniors, postbiotics can play a role in reducing inflammation and strengthening gut health.
Key benefits of postbiotics for seniors:
- Strengthen the gut barrier to prevent harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream
- Reduce inflammation and support a healthier immune response
- Aid in digestion and nutrient absorption, particularly important for older adults
- Produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that help maintain gut integrity
Sources of postbiotics:
- Fermented foods like yogurt, miso, and kimchi
- Butyrate and other SCFA-producing probiotic strains
- Fiber-rich foods that encourage probiotic fermentation
How They Work Together for Senior Health
For optimal gut health, a combination of prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics is essential. Prebiotics fuel probiotics, which in turn produce postbiotics. This cycle supports digestion, enhances immunity, and reduces inflammation, all of which are crucial for maintaining good health in senior years.
Incorporating Biotics into a Senior Diet
To support gut health, seniors should: ✔ Eat a fiber-rich diet with plenty of prebiotic foods. ✔ Include probiotic-rich fermented foods to maintain gut flora balance. ✔ Support postbiotic production with fiber and fermented foods. ✔ Stay hydrated and manage stress to improve digestion. ✔ Consult with a healthcare provider before adding supplements.
Conclusion
A thriving gut microbiome is essential for seniors to maintain digestion, immunity, and overall vitality. By incorporating prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics into their diet, seniors can enhance their quality of life, reduce digestive discomfort, and support long-term well-being. Small dietary changes can make a significant difference in gut health and overall longevity.